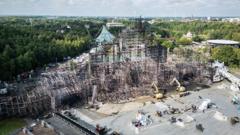Following a catastrophic fire in 2019, Notre-Dame Cathedral has been revitalized through meticulous restoration efforts, unveiling a completely overhauled architectural gem that merges traditional craftsmanship with modern techniques.
Reviving a Masterpiece: The Remarkable Restoration of Notre-Dame Cathedral

Reviving a Masterpiece: The Remarkable Restoration of Notre-Dame Cathedral
A comprehensive look into the transformation of Notre-Dame Cathedral following the devastating 2019 fire.
In a highly anticipated televised tour, French President Emmanuel Macron showcased the painstaking restoration of the iconic Notre-Dame Cathedral. The insights revealed an impressive transformation since the devastating fire that ravaged much of the historic site, undoing years of accumulated grime and soot along with the damage from flames.
One of the notable highlights is the return of the spire, which collapsed during the tragic 2019 fire. Contrary to popular belief that it was a medieval structure, the original spire was dismantled in the 1790s due to safety concerns. A neo-Gothic replica, initially erected decades later, tragically succumbed to the fire. The new spire, crafted using a blend of traditional artisan methods and advanced technology, now includes a rebuilt wooden base—the product of several hundred oak trees sourced from the forests of France.
The restoration of the cathedral also focused on cleaning and rejuvenating the limestone facade. Over 40,000 square meters of stonework has been meticulously cleaned, restoring the glow of the limestone to its original state, as experts sourced replacement stone from northern France. This process uncovered stunning fossils within the stone that celebrate Notre-Dame's storied history.
Inside, the stark contrast between old and new is evident. The once-encrusted stained-glass windows have been refurbished—dismantled, cleaned, and reinstalled to restore their vibrant colors, while many of the inner furnishings, including the grand organ with its impressive 8,000 pipes, were carefully restored after enduring fire-related pollution.
Archaeological efforts accompanying the renovations have also yielded uncovered artifacts dating back centuries, revealing the cathedral’s layered history and enriching its narrative. This includes intricate stonework believed to be part of a medieval rood-screen, a significant historical feature lost for centuries.
Despite significant progress, the restoration is ongoing, with plans for enhancements such as redesigning the surrounding esplanade and integrating a museum within the adjacent Hôtel-Dieu hospital.
As the project advances, Notre-Dame stands not only as a symbol of resilience and historical prominence but also as a testament to human artistry and dedication to preservation, promising a bright future for this emblem of Parisian heritage.
One of the notable highlights is the return of the spire, which collapsed during the tragic 2019 fire. Contrary to popular belief that it was a medieval structure, the original spire was dismantled in the 1790s due to safety concerns. A neo-Gothic replica, initially erected decades later, tragically succumbed to the fire. The new spire, crafted using a blend of traditional artisan methods and advanced technology, now includes a rebuilt wooden base—the product of several hundred oak trees sourced from the forests of France.
The restoration of the cathedral also focused on cleaning and rejuvenating the limestone facade. Over 40,000 square meters of stonework has been meticulously cleaned, restoring the glow of the limestone to its original state, as experts sourced replacement stone from northern France. This process uncovered stunning fossils within the stone that celebrate Notre-Dame's storied history.
Inside, the stark contrast between old and new is evident. The once-encrusted stained-glass windows have been refurbished—dismantled, cleaned, and reinstalled to restore their vibrant colors, while many of the inner furnishings, including the grand organ with its impressive 8,000 pipes, were carefully restored after enduring fire-related pollution.
Archaeological efforts accompanying the renovations have also yielded uncovered artifacts dating back centuries, revealing the cathedral’s layered history and enriching its narrative. This includes intricate stonework believed to be part of a medieval rood-screen, a significant historical feature lost for centuries.
Despite significant progress, the restoration is ongoing, with plans for enhancements such as redesigning the surrounding esplanade and integrating a museum within the adjacent Hôtel-Dieu hospital.
As the project advances, Notre-Dame stands not only as a symbol of resilience and historical prominence but also as a testament to human artistry and dedication to preservation, promising a bright future for this emblem of Parisian heritage.